概述
二叉查找树是一颗有序的二叉树,它有以下性质:
- 若任意节点的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值.
- 若任意节点的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于它的根节点的值.
- 可以将每个链接看做指向另一颗二叉查找树,而这棵树的根节点就是被指向的节点.
- 没有键值相等的节点.
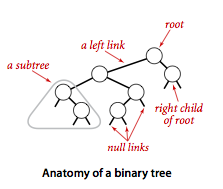
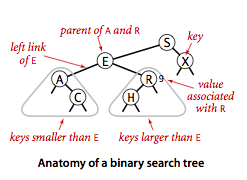
使用二叉查找树实现的符号表结合了链表插入的灵活性和有序数组查找的高效性.通常采取二叉链表作为存储结构.
每个节点都含有一个键、一个值、一条左链接、一条右链接和一个节点计数器(用于统计其所有子节点数).左链接指向一棵由小于该节点的所有键组成的二叉查找树,右链接指向一棵由大于该节点的所有键组成的二叉查找树.
如果将一棵二叉查找树的所有键投影到一条直线上,保证一个节点的左子树中的键出现在它的左边,右子树种的键出现在它的右边,那么我们一定可以得到一条有序的键列.
可以说二叉查找树和快速排序很相似.树的根节点就是快速排序中的第一个基准数(切分元素),左侧的键都比它小,右侧的键都比它大.
基本实现
|
|
在以上代码中,使用私有嵌套类Node来表示一个二叉链表,每个Node对象都是一棵含有N个节点的子树的根节点.变量root指向二叉查找树的根节点(这棵树包含了符号表中的所有键值对).
查找与插入
查找
|
|
在二叉查找树中实现查找操作是很简单而简洁的,这也是二叉查找树的特性之一.-如果树为空,就返回null,如果被查找的键小于根节点的键,我们就继续在左子树中查找,否则在右子树中查找.
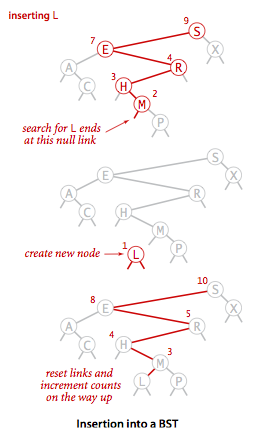
插入
插入操作的逻辑与查找差不多,只不过需要在判定树为空时,返回一个含有该键值对的新节点,还需要重置搜索路径上每个父节点指向子节点的链接,并增加路径上每个节点中的子节点计数器的值.
|
|
最大键和最小键
- 如果根节点的左链接为空,那么一棵二叉查找树中最小的键就是根节点.
- 如果左链接非空,那么树中的最小键就是左子树中的最小键.找出最大键的逻辑也是类似的,只是变为查找右子树而已.
|
|
向上取整和向下取整
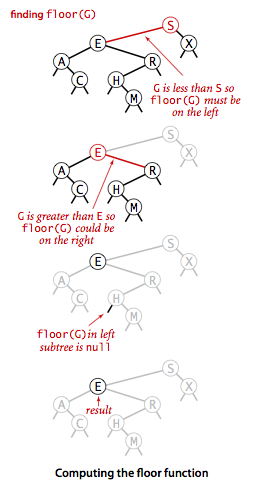
- 如果给定的键key小于二叉查找树的根节点的键,那么小于等于key的最大键
floor(key)一定在根节点的左子树中.
- 如果给定的键key大于二叉查找树的根节点,那么只有当根节点右子树中存在小于等于key的节点时,小于等于key的最大键才会出现在右子树中,否则根节点就是小于等于key的最大键.(将左变为右,小于变为大于就是向上取整的实现逻辑)
|
|
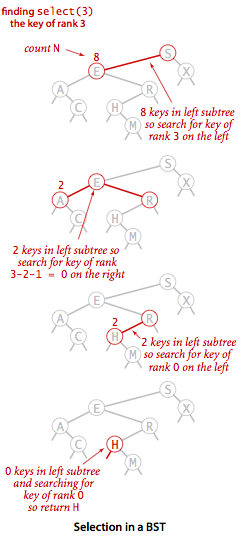
选择和排名
select
假设我们想找到排名为k的键(即树中正好有k个小于它的键).
- 如果左子树中的节点数
t大于k,那么我们就继续递归地在左子树中查找排名为k的键.
- 如果
t等于k,我们就返回根节点中的键.
- 如果
t小于k,我们就递归地在右子树中查找排名为(k-t-1)的键.
|
|
rank
rank()函数是select()函数的逆函数,它会返回指定键的排名.
- 如果给定的键和根节点的键相等,就返回左子树中的节点总数t.
- 如果给定的键小于根节点,就返回该键在左子树中的排名(递归计算).
- 如果给定的键大于根节点,就返回
t+1(根节点)加上它在右子树中的排名(递归计算).
|
|
删除最大键和删除最小键
对于删除最小键,需要不断深入根节点的左子树直至遇见一个空链接,然后将指向该节点的链接指向该节点的右子树(只需要在递归调用中返回它的右链接即可).此时已经没有任何链接指向要被删除的节点,因此它会被垃圾回收器gc掉.
删除最大键与其逻辑相似,只是方向相反.
|
|
删除
删除操作是二叉查找树中较为复杂的操作,假设我们要删除节点x(它是一个拥有两个子节点的节点),基本的实现逻辑如下.
在删除节点
x后用它的后继节点填补它的位置.找出
x的右子树中的最小节点(这样替换仍能保证树的有序性,因为x.key和它的后继节点的键之间不存在其他的键)做为x的后继节点.
- 将由此节点到根节点的路径上的所有节点的计数器减1(这里计数器的值仍然会被设为其所有子树中的节点总数加1).
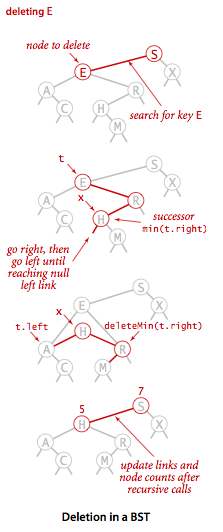
具体的过程如以下例子:
- 将指向即将被删除的节点的链接保存为
t.
- 将
x指向它的后继节点min(t.right).
- 将
x的右链接(原本指向一棵所有节点都大于x.key的二叉查找树)指向deleteMin(t.right),也就是在删除后所有的节点仍然都大于x.key的子二叉查找树.
- 将
x的左链接(本为空)指向t.left(其下所有的键都小于被删除的节点和它的后继节点).
以上的实现逻辑有一个缺点,即是在某些实际应用场景下会产生性能问题,主要原因在于后继节点是一个随意的决定,且没有考虑树的对称性.
|
|
范围查找
实现一个范围查找的思路可以是:将所有落在给定范围以内的键放入一个队列Queue并跳过那些不可能含有所查找键的子树.
|
|
总结
二叉查找树的高度决定了它在最坏情况下的运行效率,但由于键的插入顺序不会是永远随机的,所以树的某一端高度可能会非常深,解决这个问题可以使用平衡二叉查找树,它能保证无论键的插入顺序如何,树的高度都将是总键数的对数.
本文中的实现皆采用递归的方式是为了提高可读性,二叉查找树可以使用非递归的方式实现且效率会更高.
二叉查找树结合了链表插入操作的灵活性和有序数组查找操作的高效性,且还有很多种优化的改进方案(例如平衡二叉查找树),总体来说二叉查找树是一种比较好的动态查找方法.
end
- Author : SylvanasSun
- Email : sylvanassun_xtz@163.com